A researchers group from Ankara University, Ankara, Turkey, conducted research to evaluate the nutrients and nutritional elements consumed by individuals considering their adherence to the Mediterranean diet. A balanced diet provides adequate nutrition to the body for its functioning. The standard diet consists of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and micronutrients in balanced proportions. Constituents in the conventional diet vary according to regions. Diet also varies in different cultures. Over the decades, people in other areas have developed their traditional dietary habits based on region and resources. The scientific basis for conventional diets in different regions is very limited. However, it has become common knowledge that the Mediterranean diet is the healthiest of all.
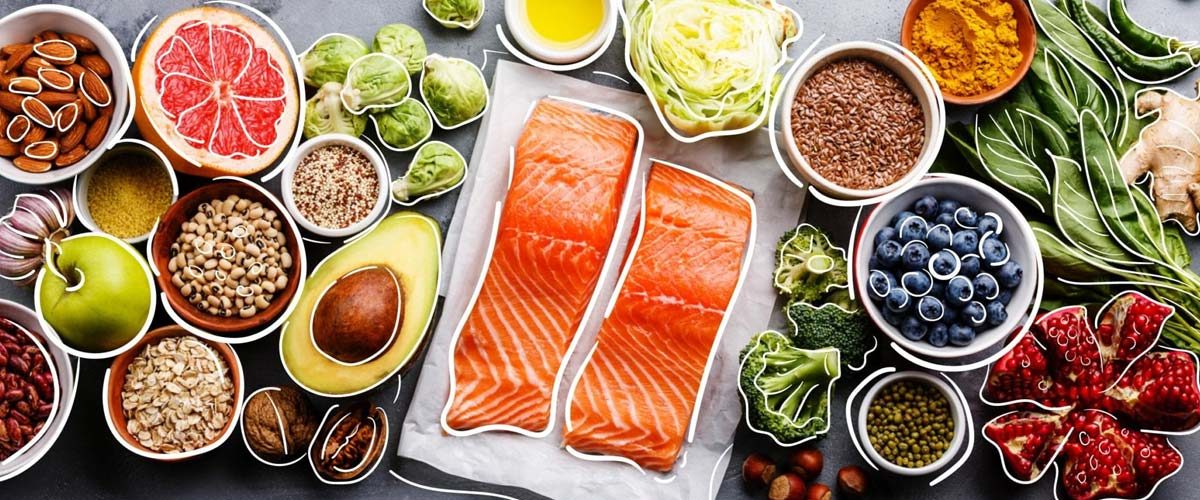
The people living on the Mediterranean coast consume a plant-based diet based on regional resources. This diet largely consists of cereals, fruits, vegetables, legumes, tree nuts, seeds, olives. The low ratio of cardiovascular disease in Mediterranean people draws particular attention to this combination of diet. The Mediterranean diet is most favorable for the aging process in humans. It decreases the risk of cardiovascular diseases and cancer. Another component of a healthy diet is the importance of breakfast. Good dietary habits can prevent disorders like obesity, type 2 diabetes, and hypertension.
There is abundant scientific evidence available for the positive impact of the Mediterranean diet. The scientific basis for the importance of breakfast is not yet established. A research study was conducted at Ankara University, Ankara, the Turkey, shows the relation between nutritional status after breakfast in adults consuming a Mediterranean diet. This study determines whether nutritional uptake is more effective in people consuming the Mediterranean diet. Researchers from Ankara University, collected samples among 400 adults aged 18 and 64. There is a variance in the level of adherence to the Mediterranean diet among the volunteers. The study concluded that more than half the participants met the criteria for moderate compliance according to the levels of adherence to the Mediterranean diet. Consumption of soup, walnut, hazelnut, peanut, almond at breakfast leads to higher compliance. The study provided the scientific basis that nutritional status after breakfast in people consuming the Mediterranean diet is not different.
The results were published in the Pakistan Journal of Nutrition.














Add comment