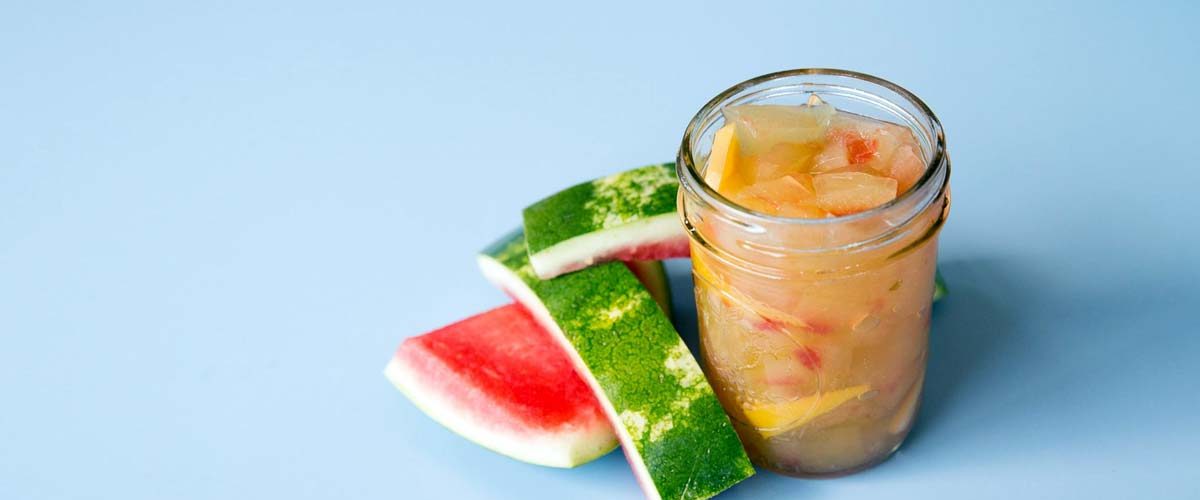
Watermelon fruit is composed of 68% of flesh, almost 2% seeds and approximately 30% rind of the total fruit mass. Inner flesh is usually of red color or green if not ripe. Watermelon fruit is considered as a rich source of vitamins A, B, C and E and minerals K, mg, Ca and Fe and antioxidants e.g., phenolics and carotenoids1.
Beneficial effects of watermelon fruit may be due to its content of bioactive compounds that have antioxidant or anti inflammatory properties2. Example of such bioactive compounds in watermelon fruit is citrulline (an amino acid) that may influence atherosclerosis3. In this context a new study was carried out with aim to prepare three samples from different parts of watermelon fruit (of Saudi origin) and to determine proximate, mineral, vitamin, flavonoids and sitosterol compositions of watermelon fruit samples4.

From the study purpose three samples were prepared from interior pulp region, exterior pulp region and from the rind of watermelon fruit. Proximate composition was determined by conventional official methods, analytical determination of minerals was performed by ICP-MS (inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrophoto meter), vitamins and flavonoids were determined by High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and β-sitosterol by Gas Chromatography (GC) techniques4.
The mineral composition in watermelon samples was calculated. Potassium concentration in flesh of watermelon fruits on water melon exterior and interior samples and in the rind also were remarkably high compared to the other minerals. It was presented that an average of 32% of the total mineral content of samples of tropical fruits and unconventional foods investigated.
Three flavonoids were determined in watermelon fruit in the study i.e. kaempferol, quercetin and rutin. Values of β-sitosterol of watermelon sample studied were lower than β-sitosterol levels in watermelon, banana, orange and avocado fruits5.
Flesh or pulp and rind are the parts of watermelon fruit that analyzed for macro- and micronutrients, flavonoids and β-sitosterol in this study. The results showed that watermelon fruit contains high percentages of moisture and carbohydrates and low percentage of fat. Potassium (and some other minerals) and vitamins C, E and B6 found in variable amounts in watermelon samples. Βeta-carotene found in high amount in the interior flesh or pulp.
Rutin which is a flavonoid and antioxidant, detected only in the interior pulp sample, while β-sitosterol (phytosterol) found in all parts of watermelon fruit. Nutrients and antioxidants investigated in the present study may make watermelon fruit a reliable food source with regard to human nutrition and health.
References:
- Perkins-Veazie, P., J.K. Collins and B. Chevidence, 2007. Watermelons and health. ActaHortic., 731: 121-128.
- Figueroa, A., M.A. Sanchez-Gonzalez, P.M. Perkins-Veazie and B.H. Arjmandi, 2011. Effects of watermelon supplementation on aortic blood pressure and wave reflection in individuals with prehypertension: A pilot study. Am. J. Hypertens., 24: 40-44.
- Poduri, A., D.L. Rateri, S.K. Saha, S. Saha and A. Daugherty, 2013. Citrulluslanatus sentinel (watermelon) extract reduces atherosclerosis in LDL receptor-deficient mice. J. Nutr. Biochem., 24: 882-886.
- Hina A. Abu-Hiamed, 2017. Chemical Composition, Flavonoids and β-sitosterol Contents of Pulp and Rind of Watermelon (Citrulluslanatus) Fruit. Pak. J. Nutr., 16: 502-507.
- Duester, K.C., 2001. Avocado fruit is a rich source of β-sitosterol. J. Am. Dietetic Assoc., 101: 404-405.














Add comment