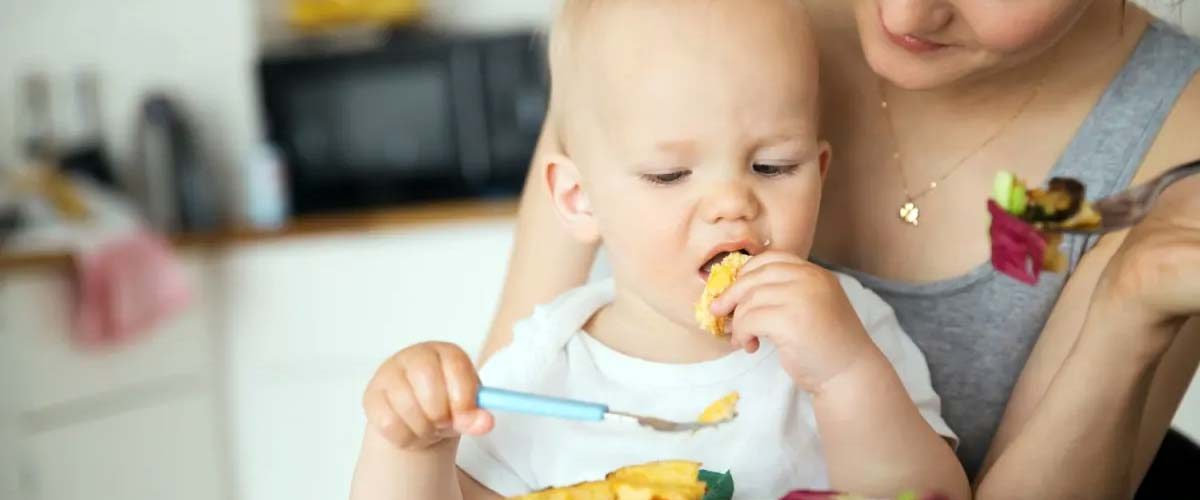
Malnutrition is a condition that results from eating a diet that does not supply a healthy amount of nutrients essential for the human body e-g calories, protein, carbohydrates, fat, vitamins, and minerals. Around 45% of deaths among children fewer than 5 years of age are linked to malnutrition and this condition puts children at greater risk of dying from common infections increases the severity of such infections, and delays recovery. These conditions mostly occur in low- and middle-income countries.
Indonesia is the 4th most populous country where the malnutrition rate in children is 19.6% and it is a serious health concern in Indonesia. Food refusal and eating hitches are the major barriers to the fulfillment of nutritional needs. Malnutrition weakens the immunity in the toddlers that enhances the emergence of several diseases in the body.
Eating complications in children who do not receive immediate treatment could cause, dehydration, malnutrition, electrolyte imbalances, anxiety disorders, mental developmental disorders, and sometimes lead to life-threatening possibilities.
Research has been conducted by Darwati et al. (2014) in Jayapura showed that more than 90% of children had eating problems due to inappropriate feeding practices. The prevalence of eating difficulties was 33-44 % of all of the children suffered from mild to moderate malnutrition.
The causes of food refusal and eating difficulties may vary depending upon the biological interactions and environmental factors, especially family factors. The most common cause of malnutrition in children is the lack of nutrition intake due to the texture and composition of food and the feeding rules. The mother’s lack of awareness of food willingness signs in her baby is also a major cause. Therefore, mothers need to realize the willingness of their baby’s oromotor before giving food such as how to give breast milk, complementary foods, and suitable milk formula to avoid eating difficulties in children.
In this regard, a research was conducted by Hizn et al. (2020) to observe the eating patterns of children, diminish the frequency of eating refusal and optimize children’s nutritional status. The team of researchers found that the food refusal in children is the result of mothers’ improper feeding practices. Proper feeding practices in earlier stage leads to less frequent food refusal in children will be. They recommended that the increase in knowledge and skills must be taught to mothers continuously until they reach the optimum results.















Add comment